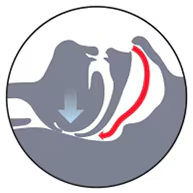
Quali sono le cause del russamento?
È davvero possibile “curare” il russare? E se si russa, perché è importante conoscerne il motivo?
Il russare può anche essere il segno di un grave disturbo: l'apnea ostruttiva del sonno (OSA).
L’OSA è un disturbo respiratorio del sonno caratterizzato da pause respiratorie chiamate apnee. Queste durano da 10 a 30 secondi e possono verificarsi più di 30 volte all’ora. Le apnee causano frequenti micro risvegli che disturbano il sonno e influenzano la qualità della vita e della salute. L’OSA colpisce circa il 3-17% della popolazione maschile, ma oltre l’80% dei pazienti non viene diagnosticato6.
Bibliografia:
- Ohayon, M.M., et al., Snoring and breathing pauses during sleep: telephone interview survey of a United Kingdom population sample. BMJ, 1997. 314(7084): p. 860-3.
- A+A Healthcare study undertaken with 95 patients who wore Narval CC (Equinox in France) in 2011.
- Hu, F.B., et al., Prospective study of snoring and risk of hypertension in women. Am J Epidemiol, 1999. 150(8): p. 806-16.
- Lechner, M., et al., Snoring and breathing pauses during sleep: interview survey of a United Kingdom population sample reveals a significant increase in the rates of sleep apnoea and obesity over the last 20 years – data from the UK sleep survey. Sleep Med, 2019. 54: p. 250-256. You can say that 1 in 5 snorers (men or women) could suffer from sleep apnea.
- Vecchierini MF & al. A custom-made mandibular repositioning device for obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea syndrome: the ORCADES study. Sleep Med. 2016 Mar;19:131-40. doi: 10.1016.
- Young T, Evans L, Finn L, Patta M. Estimation of the clinically diagnosed proportion of sleep apnoea syndrome in middle-aged men and women. Sleep 1997; 20: 705-706.
- Sleep-disordered breathing affects 34% of men and 17% of women aged between 30-70 Peppard et al. Increased Prevalence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Adults. Am J Epidemiol. 2013 (5.17).